Aerobic exercise
Cardiorespiratory fitness can be measured using VO2 max, a measure of the amount of oxygen the body can uptake and utilize. Aerobic exercise, which improves cardiorespiratory fitness and increases stamina, involves movement that increases the heart rate to improve the body's oxygen consumption. This form of exercise is an important part of all training regiments ranging from professional athletes to the everyday person.
Prominent examples of aerobic exercises include:
- Jogging – Running at a steady and gentle pace. This form of exercise is great for maintaining weight and building a cardiovascular base to later perform more intense exercises.
- Working on elliptical trainer – This is a stationary exercise machine used to perform walking, or running without causing excessive stress on the joints. This form of exercise is perfect for people with achy hips, knees, and ankles.
- Walking – Moving at a fairly regular pace for a short, medium or long distance.
- Treadmill training – Many treadmills have programs set up that offer numerous different workout plans. One effective cardiovascular activity would be to switch between running and walking. Typically warm up first by walking and then switch off between walking for three minutes and running for three minutes.
- Swimming – Using the arms and legs to keep oneself afloat in water and moving either forwards or backward. This is a good full-body exercise for those who are looking to strengthen their core while improving cardiovascular endurance.
- Cycling – Riding a bicycle typically involves longer distances than walking or jogging. This is another low-impact exercise on the joints and is great for improving leg strength.
Anaerobic exercise
Anaerobic exercise features high-intensity movements performed in a short period of time. It is a fast, high-intensity exercise that does not require the body to utilize oxygen to produce energy. It helps to promote strength, endurance, speed, and power; and is used by bodybuilders to build workout intensity. Anaerobic exercises are thought to increase the metabolic rate, thereby allowing one to burn additional calories as the body recovers from exercise due to an increase in body temperature and excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) after the exercise ended.
Prominent examples of anaerobic exercises include:
- Weight training - A common type of strength training for developing the strength and size of skeletal muscles.
- Isometric exercise - Helps to maintain strength. A muscle action in which no visible movement occurs and the resistance matches the muscular tension.
- Sprinting - Running short distances as fast as possible.
- Interval training - Alternating short bursts (lasting around 30 seconds) of intense activity with longer intervals (three to four minutes) of less intense activity.
Training
- 100 m sprint: In a sprint, the athlete must be trained to work anaerobically throughout the race, an example of how to do this would be interval training.
- Century ride: Cyclists must be prepared aerobically for a bike ride of 100 miles or more.
- Middle distance running: Athletes require both speed and endurance to gain benefit out of this training. The hard-working muscles are at their peak for a longer period of time as they are being used at that level for the longer period of time.
- Marathon: In this case, the athlete must be trained to work aerobically, and their endurance must be built-up to a maximum.
- Many firefighters and police officers undergo regular fitness testing to determine if they are capable of the physically demanding tasks required of the job.
- Members of armed forces are often required to pass a formal fitness test. For example, soldiers of the U.S. Army must be able to pass the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT).
- Hill sprints: Requires a high level of fitness to begin with; the exercise is particularly good for the leg muscles. The Army often trains to do mountain climbing and races.
- Plyometric and isometric exercises: An excellent way to build strength and increase muscular endurance.
- Sand running creates less strain on leg muscles than running on grass or concrete. This is because sand collapses beneath the foot, softening the landing. Sand training is an effective way to lose weight and become fit, as more effort is needed (one and a half times more) to run on the soft sand than on a hard surface.[citation needed]
- Aquajogging is a form of exercise that decreases strain on joints and bones. The water supplies minimal impact to muscles and bones, which is good for those recovering from injury. Furthermore, the resistance of the water as one jogs through it provides an enhanced effect of exercise (the deeper you are, the greater the force needed to pull your leg through).
- Swimming: Squatting exercise helps in enhancing a swimmer's start.
For physical fitness activity to benefit an individual, the exertion must trigger a sufficient amount of stimuli. Exercise with the correct amount of intensity, duration, and frequency can produce a significant amount of improvement. The person may overall feel better, but the physical effects on the human body take weeks or months to notice—and possibly years for full development. For training purposes, exercise must provide a stress or demand on either a function or tissue. To continue improvements, this demand must eventually increase little over an extended period of time. This sort of exercise training has three basic principles: overload, specificity, and progression. These principles are related to health but also enhancement of physical working capacity.






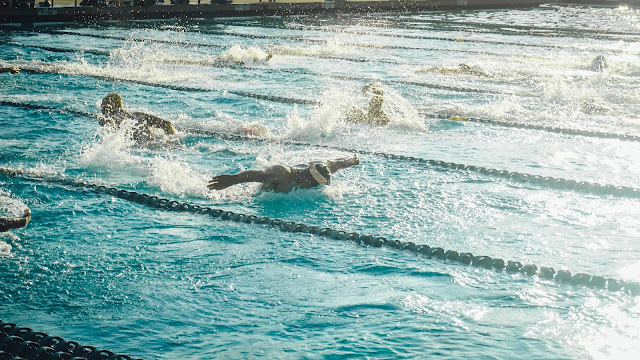

0 Comments
If you have any querry, let me know.